Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
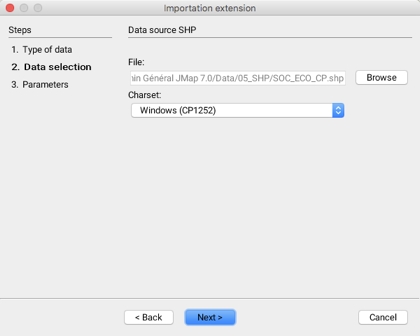
The second step in importing data from SHP files involves selecting the data sets to import.
File
Select the SHP file to import.
Windows (CP1252)
Drop-down menu to select the character set used for the attributes stored in the DBF file. If this parameter is not properly defined, it is possible that some characters will not be properly displayed. The default value is CP1252, this value is appropriate most of the time.
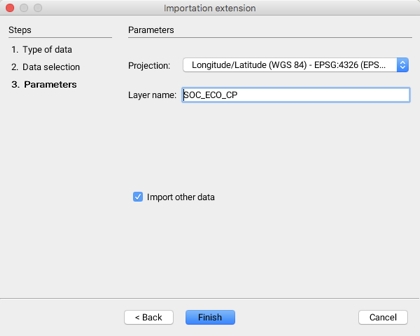
The third step allows you to configure the parameters of the layer that will be generated when the data is imported.
Projection
Drop-down menu allowing you to select the data projection. It is possible to select None. The JMap administrator determines which projection systems will be available to the user.
Layer name
The data will be imported into a layer whose name must be specified.
Import other data
It is possible to indicate that other data sets will be imported; this automatically brings you back to the first step.
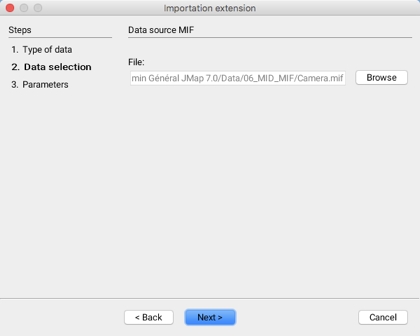
The second step in importing data from MIF files involves selecting the data sets to import.
The third step allows you to configure the parameters of the layer that will be generated when the data is imported.
Projection
Drop-down menu allowing you to select the data projection. It is possible to select None. The JMap administrator determines which projection systems will be available to the user.
Layer
The data will be imported into a layer whose name must be specified.
Import other data
It is possible to indicate that other data sets will be imported; this automatically brings you back to the first step.
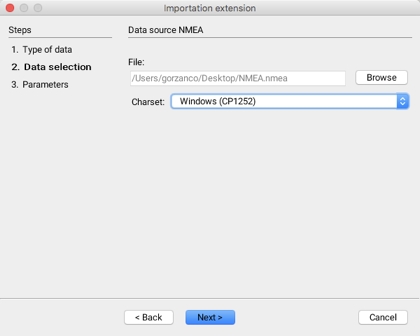
The second step in importing GPS data that meets NMEA standards involves selecting the data sets to import.
File
Select the NMEA file to import.
Windows (CP1252)
Select the character set used for the sentences of the NMEA file. If this parameter is not properly defined, it is possible that some characters will not be properly displayed. The default value is usually appropriate.
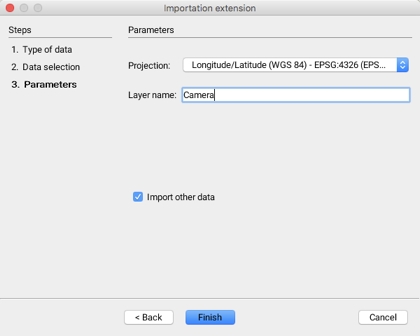
The third step allows you to configure the parameters of the layer that will be generated when the data is imported.
Projection
For all NMEA sentences, the coordinates system is based on the WGS84 ellipsoid. The proposed projection therefore includes this ellipsoid.
Layer name
The data will be imported into a layer whose name must be specified.
Import other data
It is possible to indicate that other data sets will be imported; this automatically brings you back to the first step.
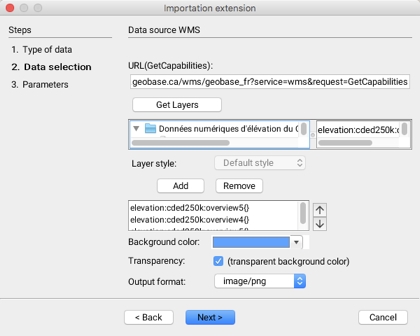
The second step in importing raster data from servers that comply with the WMS standard involves selecting the data sets to import.
URL(GetCapabilities)
Get Layers
This button allows you to obtain the list of raster data sets contained in the server. On the left, the data sets are organized hierarchically. When a data set is clicked, its details are displayed on the right.
Layer style
For certain data sets, a style can be selected from a drop-down menu.
Add / Remove
These buttons allow you to add or remove data from the selection.
Background color
A background color can be selected and will be displayed where there is no data.
Transparency
The background color can be made transparent.
Output format
This drop-down menu allows you to choose the layer output format. This is always an image whose format can be selected among the options offered by the WMS server.
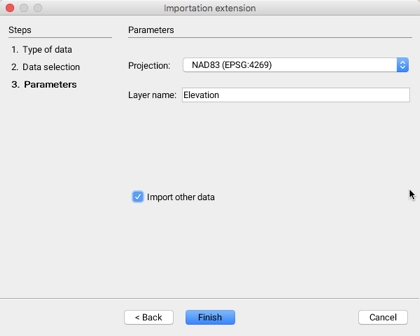
The third step allows you to configure the parameters of the layer that will be generated when connecting to the WMS server.
Projection
Drop-down menu allowing you to select the data projection. The available projections are determined by the WMS server. The projection of the data must be the same as that of the project because JMap does not perform the reprojection of the data in raster format.
Layer name
Data will be imported into a layer whose name must be specified. By default, the name is derived from the names of the data sets to import.
Import other data
It is possible to indicate that other data sets will be imported; this automatically brings you back to the first step.
You must indicate the GetCapabilities URL that will return the WMS server capabilities. The URL must be similar to the following example:
JMap Importation extension allows users of the JMap Pro application to import spatial vector and raster data sets and to add them as a layer in a project.
This layer is ephemeral and will disappear when the session is terminated. However, the contents of this layer can be copied to an editable project layer or to a personal layer.
For more information on copying elements from one layer to another, refer to the JMap Edition User Guide.
For more information on personal layers, refer to the JMap Pro User Guide.
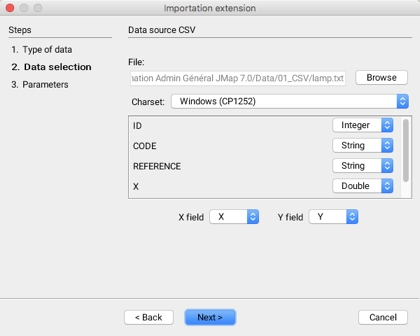
The second step in importing CSV data involves selecting the data set to import and its structure.
File
Select the CSV file to import.
Windows (CP1252)
Drop-down menu to select the character set used for the attributes stored in the CSV file. If this parameter is not properly defined, it is possible that some characters will not be properly displayed.
Attributs
Select, for each file attribute, the type of data it contains, either String, Double or Integer.
X field - Y field
Select the attributes of the file corresponding with the x and y coordinates.
The third step allows you to configure the parameters of the layer that will be generated when the data is imported.
Projection
Drop-down menu allowing you to select the data projection. It is possible to select None. The JMap administrator determines which projection systems will be available to the user.
Layer name
The data will be imported into a layer whose name must be specified.
Import other data
It is possible to indicate that other data sets will be imported; this automatically brings you back to the first step.
The graphical interface of the Importation extension, which can be accessed by going to Tools -> Import data in the Pro application, guides the user through the steps of the importation process.
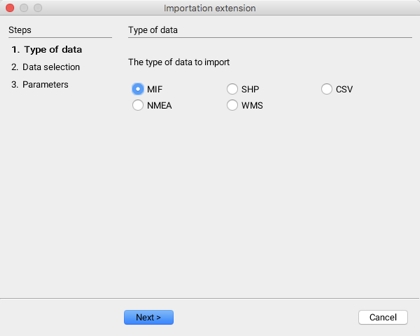
Importation involves three sequential steps:
Selecting the type of data,
Selecting the data sets to import and
Configuring the parameters associated with each type of data.
Five types of data formats can be imported:
MIF files, usually produced by MapInfo applications;
SHP files, usually produced by ESRI applications;
CSV files, which are text files with separate values containing X and Y geographical coordinates;
GPS data structured according to the NMEA standard; and
Raster data from servers that are compliant with the WMS standard.
The subsequent steps vary according to the format type of the data to import.