Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
The configuration interface of a project allows you to access information on the project. This interface also contains functions to configure various parameters, such as the initial view of the project in the applications.
1
2
General information configured when creating the project.
3
Project settings. The project’s parameters. They are configured when the project is created. The project’s extent corresponds to the extent of the layers that make up the project. When the project does not have any layers, the values are equal to 0.
4
5
6
References. This section indicates the deployed applications that use this project.
7
8
9
10
Layers. This section shows a list of the project layers and their statuses. Shortcuts allow you to access the interfaces to add and organize layers.
11
The project preview provides a preview of the map, in which you can test the configurations made as they work in JMap Server applications.
JMap Server Lima does not provide a JMap Pro preview of your project. The function of this preview is replaced by the Administration extension displayed when creating a JMap Pro application. The JMap Pro Applications section provides details of this extension.
It opens a JMap Web application in a new browser window.
The preview offers most of the functionality of JMap Web applications and allows you to validate the project’s configuration.
The JMap Web preview does not allow data editing. Data editing can be done in a JMap Web type application.
It opens a JMap NG application in a new browser window.
The preview offers most of the features of JMap NG applications and allows you to validate the project configuration.
The JMap NG preview does not allow data editing. Data editing can be done in a JMap NG type application.
The project sections are organized into tabs: and , , and the configuration interfaces of .
Initial view settings. These parameters are specified when the project is created. The initial view is defined by clicking on in the Preview section. By default, the initial view corresponds to the extent of the project. When the project does not have any layers, the values are equal to 0.
Extensions. This section presents the list of JMap extensions configured for the project. The switch next to the name of each extension enables or disables the extension in the JMap NG and JMap Survey applications which publish the project. The section provides more details on this topic.
Mapbox cache. This section presents the size of the cache for the project’s vector tiles. It also indicates if you want to automatically delete the cache of the vector tiles. You can clear the cache by clicking on .
This section allows you to the project with JMap Cloud.
Preview. This section displays when the project contains at least one layer. It shows a map preview, and you can zoom in or out on it. Click on to open a or a in a separate window in which you can define the initial view and test the project configurations. You can select a base map for the JMap Web preview: None, OpenStreetMaps, Mapbox maps, and Bing maps, if they are available for your organization.
These buttons allow you to the project, access or edit it.
JMap Web preview also allows you to configure the initial view of the project when it is opened in JMap Web applications. To do this, click on and then on Initial extent. A rectangle displays to delimit the initial extent.
Click on Maximum extent to display the maximum extent. When you close the preview, the geographic coordinates of the initial extent are automatically saved.
In JMap, map data is organized in projects. A project is composed of an ordered list of layers. Typically, when a JMap application connects to JMap Server, the application opens a project and displays the project layers. You can create as many projects as you want.
Each layer of a project is associated with a spatial data source. The data source provides the data of the layer. Different projects can contain layers sharing the same data sources, allowing different data bindings, styles, etc. for the same data. Also, more than one layer in a project can share the same data source. This is useful when using layer filters to show different data of the same data source on multiple layers.
A project is a secured resource, which means that permissions are associated with it in order to control access by users. This allows precise control of which users or groups will be allowed to open each project. Similar access control is also available for each layer in the project.
The Projects section in Resources displays a table that shows the projects configured in the server. In this section you can create a new project, access the configuration interface of a project by clicking on its name as well as manage projects that you select in the table.



The Permissions button appears in the Projects section and is enabled when at least one project is selected. It is also displayed in the project configuration interface.
This section has two tabs: Permissions and Owners. The owners are the only ones who can manage the administrative permissions for the project, manage the list of owners and delete it.
A list of users and groups with permissions appears in the Permissions tab. Click on to add new users or groups.
Available users and groups are configured in the JMap Server section of JMap Admin. Refer to the Users and Groups section for more information about managing users in JMap Server.
Project permissions are divided into two categories: administrator permissions and user permissions.
Administrator project permissions define the project administration rights for the users authorized to use JMap Admin. For more information on concepts related to permissions and administration roles in JMap Admin, refer to the Managing Permissions section.
Administrate project
Allows an administrator to modify the project and its content.
Access project
Allows an administrator to access a project to view its content and to use it when deploying JMap applications.
User project permissions determine which users and groups can open a project. Access will be denied to users who do not have the appropriate permissions. Security can also be configured at the layer level. For more information on this topic, refer to the Layer Permissions section.
Open this project
Allows a user to open a project from a JMap application.
Adding the Anonymous user to the list of users authorized to open the project gives users the possibility to open a project without any authentication. This is equivalent to removing all security for opening the project. This is useful for public applications, when no project access control is needed.
Adding the Everyone user to the list of users authorized to open the project allows all users to open the project, including the Anonymous user. This means that the project is accessible to all users, with or without authentication.
Adding the Authenticated users to the list of users authorized to open the project allows any authenticated user to open a project. This is useful for private applications where all users are allowed to open a project but must authenticate themselves.
To create a new project, press Create in the Projects section. Projects are created by walking through a wizard.
Identification
Name
Enter a name for the new project. The name must be unique.
Description
Optionally enter a description for the new project. Used for administrative purposes.
Default language
Available languages
Usage statistics
Select this option if you wish to obtain usage statistics regarding this project, the layers it contains, and the public contexts that are created in the JMap Pro applications deployed from this project.
Automatically invalidate Mapbox tile cache
Parameters
Map projection
Determines how the data will be displayed in the client applications. Any data that is in a different projection will be converted on the fly to this projection. Note that changing the map projection of a project invalidates the layer cache. This can temporarily reduce the performance of applications.
Map unit
The map unit is automatically selected according to the selected map projection.
Display unit
The unit used to display map coordinates.
Measurement
Geodetic: Distance and area measurements will be made using spherical calculations based on the projection’s ellipsoid. Cartesian using: Distance and area measurements will be made from calculations on the two-dimensional plane using the specified projection.
Distance unit
The unit used to display distances (measurements, zoom levels, etc.).
Minimum scale
The minimum scale of the map. Users cannot zoom out further when this limit is reached. When you check this option the default value is 1:1.
Maximum scale
The maximum scale of the map. Users cannot zoom in further when this limit is reached. When you check this option the default value is 1:1.
Background color
Default color to use for the background of the map.
Default selection color
Color of selected objects on the map. It can also be defined for each layer.
When creating a project, you can either create a new empty project or import an existing project configuration from another source. When you use an existing configuration, you can automate the creation of the project’s layers and avoid reconfiguring everything in JMap Admin.
Currently only one option is available for importing a project configuration: importing projects from an ESRI ArcGIS REST Service.
You can choose to import the layer configuration from an ESRI ArcGIS REST service. JMap will import the project’s parameters, the layers and their symbology, the scale parameters, the extents, etc.
Select the ArcGIS REST option and click on Next.
ArcGIS REST
URL
Username
Enter the username to authenticate and log in to the ArcGIS REST service.
Password
Enter the password to authenticate and log in to the ArcGIS REST service.
Layers
Select the layers whose configurations you wish to import. JMap creates a layer in the project for each imported layer. The configuration of the JMap layer is similar to that of the original layer, but there may be some differences.
JMap supports the import of OGC WMTS raster layers.
In the REST service layer import interface, icons indicate layers whose format is not compatible with JMap.
Attribute queries are used to find and select elements of a map layer using their attribute values or a database associated with the layer.
In JMap Admin, JMap administrators create the queries and their associated forms. Then, users of JMap applications use those forms to enter attribute values to search for. All elements whose attribute values match the values entered are then selected or listed in an elements explorer.
The Queries tab of a project's configuration interface allows you to configure the project's queries.
The Queries tab appears when the project contains at least one layer.
This tab presents a table that displays the query groups. The table shows the number of queries each group contains. The section provides details about the groups.
To create a new query you must position yourself in a group of the Queries tab. The Create a query button is displayed and you can therefore open the query configuration interface.
Parameters will vary depending on the type of query selected.
This type of query is used when the search must be conducted within the data of an external database. The external database must contain a field that links to a layer attribute. A select SQL query is executed in the external database and the values returned are then associated with the layer elements using the link field.
Although search forms are designed to mark fields as required or optional, the where clause of the query must be adjusted to support this option. To accomplish this, any part of the query that is associated with optional parameters must be included between braces ( { } ).
Example of WHERE clause:
CITY = '$param1' and { COUNTRY = '$param2' }
$multiple{true|false} {$delimiter{;}}
Example:
CITY = '$param1{$multiple{true} $delimiter{;}}'
Searches for cities whose CITY attribute value is equal to one of the values entered in parameter 1. The values are separated by semicolons.
Attribute queries can be modified by administrators. In JMap Dakar and later versions, when a project’s queries are modified, the applications that disseminate the project do not need to be redeployed because the changes are reflected directly.
Attribute queries can be organized into groups. This is particularly useful for projects that have a large number of queries.
To create a new group, click on the Create group buttonon the Queries tab.
To delete a group, select it in the list and click on Delete.
Deleting an attribute query permanently deletes the query and its associated form. To delete a query, select it in the list and click on Delete.
Once a query has been created, it is automatically published. However, you can disable this publication, which will make your query unavailable in applications, but its configuration will still be saved. If you do not want your query to be published, clear the Published checkbox of your query in the query management interface.
When a project contains referenced layers, the queries configured on these layers are automatically available in the project. The project “inherits” these queries.
You cannot modify these queries from the project; they can only be modified in the project that contains the original layer.
If you wish to make changes to a query on a referenced layer, create a copy of the query by clicking on Clone. The configuration interface shows the search parameters that you can modify.
Once the new query has been configured, you can clear the Published check box of the query that was “inherited” from the referenced layer if you no longer want it to be available in JMap applications. If the Published check box is cleared for an attribute query on a layer, that query will no longer be available in the projects that use the referenced layer.
Among the languages available, select the one that will be used by default when the requested language is unavailable or when translations are missing. For more information, refer to the section.
Select one or more languages that will be supported by the project. All text elements in the project’s configuration (name of project, names of layers, mouseover bubbles, etc.) will have to be translated into each supported language. At least one language must be selected. For more information, refer to the section.
Select this option if you want to automatically invalidate the Mapbox tile cache. Mapbox is used to produce vector tiles for some of the project’s layers and thus improve the performance and rendering of JMap Survey and JMap NG applications. Refer to for more information on this topic. Mapbox vector tiles can be produced in advance and cached. The following offers details on how to create and manage the Mapbox cache. The Mapbox cache is automatically deleted when: a layer is published, a published layer is deleted, attributes that are bound to a layer are added or deleted, a layer’s base filter changes, the spatial data source of a layer changes, or the project is deleted. The Mapbox cache is not automatically deleted when: an unpublished layer is added to the project, an unpublished layer is deleted from a project, minor changes are made to a layer (style, thematics, mouseover), or the order of attributes bound to a layer changes.
Enter the URL of the ArcGIS Server REST service. Exemple Afterwards, click on Load to show the list of available layers.
This example searches for cities for which the attribute value CITY is equal to the value of parameter 1 ($param1) entered by the user and who optionally have their value for the COUNTRY attribute equal to the value of parameter 2 ($param2) entered by the user. If parameter 2 is left blank , the entire block { COUNTRY = '$param2' } is removed from the query, along with the and operator, which is now an orphan. Note that the administrator must absolutely define $param2 as optional when designing the form. Refer to the section for more information on designing forms.
Multiple values can be entered with a type field in the forms. The values are separated by the delimiter character ; (semicolon). This option can be activated in the WHERE clause of the query. The syntax is as follows:
To modify the order of groups, click on Modify and select Reorder groups. The window that is displayed allows you to drag and drop the groups in order to change their order. To rename a group, click on .
You can also create a new query on a referenced layer as described in the section .
Database
Select the database in which you would like to perform your query.
SQL query
Enter the SQL query that will be executed in the database to search for elements.
Example
select * from cities where CITY_LANGUAGE='$param1'
Searches the database selected above, in the cities table. Retrieves all fields of records for which the value of the CITY_LANGUAGE field is equal to the value entered by the user ($param1).
Layer attribute
Among the layer attributes, indicate which one is used to link with the database.
Field
Among the fields returned by the SQL query, indicate which one is used to link with the layer.
Form layout
Click on this button to configure the query form. Refer to the Forms section for more information on this topic.
Title
Enter a title for the query. Users will see this title in a list of queries.
Layer
Select the layer on which the query will be executed. A search field is provided to simplify layer selection.
Maximum scale
Specify the maximum scale used to present the results on the map. This is used to avoid zooming in too closely on the results.
Max. returned values
Specify the maximum number of elements this query can return. The query will refuse to execute if the return size is higher than this limit. This is used to avoid very long queries that could slow down the system.
Query templates
Basic: With this type of query, the search is only performed on the layer attributes. This is the simplest type of query. External database: With this type of query, the search is performed in an external database that has a field linking to an attribute of the layer. Setting up this type of query is more complex but offers more searching flexibility.
WHERE
WHERE clause of the SQL query used to run the search. Here is where all the search criteria will be defined. Typically, this clause contains numbered parameters ($param1, $param2, etc.) that will be replaced by the values the user enters in the form.
Examples
COUNTRY='$param1'
Selects the layer elements for which the attribute value COUNTRY is equal to the value entered by the user.
The attribute value must perfectly match the value entered ($param1).
lower(COUNTRY) like lower('$param1%')
Selects the layer elements for which the attribute value COUNTRY is similar to the value entered by the user. The attribute value must begin with the value entered ($param1). Since the lower operator is used, the search is not case sensitive.
POP2000>=$param1 and POP2000<$param2
Selects layer elements that have the POP2000 attribute value within the range defined by the two values that were entered ($param1 and $param2).
Form layout
Press this button to configure the query form. See Forms for more information.
The image producer of a JMap project is used to produce images on demand for that project. These images are used for JMap Web applications. When a user works in JMap Pro, the image producer is not used because the data is transferred in vector format (except for photos).
Normally, the image producer’s settings do not need to be modified because the default configuration is adequate. The following table describes the settings of the image producer.
Memory settings
Maximum size
The maximum amount of memory allotted to the project’s image producer. This memory is used to store the project’s vector data in order to accelerate the production of images. For very large projects, this setting can be increased.
Memory usage
The amount of memory currently used. The left value varies depending on usage. The right value is the maximum amount of memory allocated to the image producer.
Usage peak
Maximum memory size reached since last JMap Server startup.
Memory release
Determines the percentage of memory to be released when the memory of the image producer is saturated.
Thread pool settings
Initial size
The number of threads determines the number of images that can be produced simultaneously.
Maximum size
If the number of threads increases due to high demand, this value limits the number of threads.
Pool usage
Number of threads currently used (left value) out of the maximum number allocated (right value).
Usage peak
Maximum number of threads reached since last JMap Server startup.
View wait timeout
The maximum period before an image request expires. This option is usually disabled.
Extensions which are compatible with JMap NG and JMap Survey applications must be configured and activated on the project to make them accessible to the users of these applications.
To configure the extension, in the project configuration interface select the tab with the extension name. Once the configuration is complete, press Save.
To activate the extension, slide the extension switch in the Extensions section of the project configuration interface.
The Installed Extensions section provides details on configuring extensions in JMap Server.
The Projects section offers buttons to create, clone or delete projects. Other functions are avalilable from the project configuration interface.
A project can be modified by pressing Edit from the project detail section. Modifying a project goes through the same steps as when the project was created.
If the projection of the project is changed, the vector data cache of the layers is cleared.
You can clone an existing project by selecting it from the table and pressing Clone. All layers inside the project are copied to the new project.
The underlying spatial data sources and databases are not copied. Instead, they are shared between the layers of the new project and the layers of the old project.
You can delete an existing project by selecting it in the table and clicking on Delete. You can also delete a project from its configuration section.
Deleting a project permanently deletes all layer configurations included in it. The spatial data sources are not affected.
The layers of a project are displayed in the Layers tab of the project configuration interface. This icon located in the Layers section of the project interface also takes you to the Layers tab.
The table shows basic information about each layer of the project. When you click on the name of a layer, a details section displays.
In this tab you can define the order of layers in the project. The Organizing Layers section offers details on this topic.
Buttons allow you to perform management tasks for the layers you select in the table, as well as add new layers to the project.
Create
Clone/Reference
Import…
The icon in the Layers section of the project configuration interface gives you the three options to add a layer to the project.
When you select one or more layers you can grant permissions for the whole set. Refer to Layer Permissions.
Update data sources
Updates the spatial data sources associated with the selected layers. Refer to Spatial Data Sources.
Update caches
Update - Bulk edit…
You can edit different settings for a set of layers. You must select the layers to modify in the List tab of the Layers section of the project. Afterwards, press the Update button, and click on the Bulk edit… option. The Bulk edit interface will open.
Change ‘Antialiasing’
Check if you want to change this setting.
Change Minimum scale
Check to change the minimum scale for displaying layers.
Check Infinity or 1: and in this case, indicate the scale.
Change Maximum scale
Check to change the maximum scale for displaying layers.
Check Zero or 1: and in this case, indicate the scale.
Change Request mode
Check to change the data request mode.
Check the option of your choice.
Change Description
You can write a new description for the layers.
This button allows you to synchronize the selected layers with JMap Cloud. The section Sharing layers with JMap Cloud provides details on the subject.
Deletes the selected layers.
JMap projects can be configured to support several languages. This way, each user can view the project in his or her own language, as long as the language is available and the translations have been provided. When a JMap application is launched, it can automatically identify the language of the user’s operating system and use this language for the project and graphical interfaces. This behavior depends on the options selected when deploying the application.
For a project supporting multiple languages, each text element that is visible to the users can be translated into each language. For example, you can provide translations for the project name, the names of the layers, labels, mouseover bubbles, forms, etc.
To enable multilingual support, you must choose at least 2 languages when creating or editing a project. You must also select the default language.
Afterwards, you can enter the translations in the sections identified with the symbol when configuring the project and layers.
If translations are not provided in all available languages for certain text elements, the text will automatically be displayed in the default language.
Vector tiles are a format of vector data that is very effective for web-based mapping. With vector tiles, the entire vector data of a project is divided into tiles, similarly to raster data tiles (WMTS).
There are several standards for creating vector tiles. Mapbox has provided a standard based on the protocol buffer encoding (“Protobuf”) created by Google (). Mapbox vector tiles (mvt) are supported by a wide range of map-based products, including JMap 7 as of the Jakarta version.
A grid defining the tiling is applied to the vector data, which is split into tiles. Each tile can contain the vector data (vectors) of several layers.
A set of tiles is produced for each scale level. Generally, there are 23 scale levels in web-based mapping, 0 being Earth level and 22 being street level. The vectors of lower levels are simplified (generalized) to optimize the display of the data, while maintaining a volume of tiles that performs well.
The vectors (lines, polygons) of each layer are clipped at the boundaries of the tiles. When a geometry crosses over the boundary between tiles, it is cut, and each tile thus contains part of the geometry. The map application reunites the vectors to obtain the full geometry.
The attributes of map elements are included in the tiles. This makes it possible to display thematics created on the fly or to display data in a map using attribute filters, for instance. This makes the data more dynamic and interactive.
The vector tiles contain the geometries and their attributes; styles are not included in the tiles. The information defining the styles is stored and managed in a separate JSON file. This feature allows application users to define styles dynamically, since the applications manage the styles. In addition, when the style of the data changes, it is not necessary to generate new tiles.
Tiles can be created in advance and cached; the server responds much more quickly to queries from the web-based mapping application, and therefore the rendering of the map is very smooth and performs well. In addition, the tiles can be used with for smooth and efficient rendering, especially in 3D.
A JMap project generates three sets of data that are used by the applications:
1 JSON style file. This file accompanies the vector tiles. It contains the definition of each layer contained in the vector tiles, their style parameters, the thematics, etc.
A set of vector tiles containing the geometries and attributes of non-editable layers. JMap produces an MVT file for each tile. These tiles can be created on request when users navigate through the JMap Survey or JMap NG applications. They can also be created in advance and cached. The following offers details on how to create and manage the cache of tiles with JMap.
GeoJSON vector data corresponding to the geometries and attributes of editable layers. This data is sent to applications on request, by region.
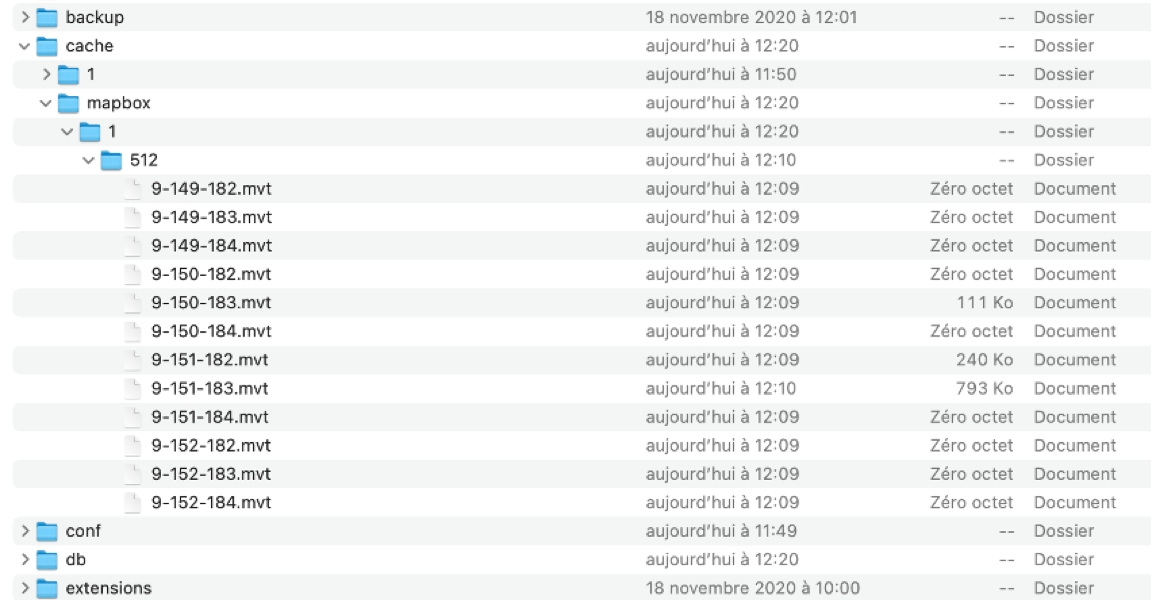
Regardless of the procedure used to create tiles (on request or in advance with caching), the tiles are created in the cache/mapbox directory of JMap Server. In this directory, there is one folder per project (named using the project ID), which contains one folder per resolution (currently 512). The files of the tiles are named using the z-x-y.mvt code, where z is the scale level, and x and y indicate the position of the tile in the grid.
In general, vector tiles are lighter than raster tiles, but some factors can affect the size of tiles and impact the performance of the JMap Survey and JMap NG applications. The size of tiles is associated with the time it takes to produce them, their storage volume, the volume of data exchanged with the applications, and the dedicated memory of the applications.
Some factors to consider:
Number of attributes bound to layers: the attribute data influences the size of the tiles; the more attributes there are, the more the size increases.
Layer visibility scales: Establishing visibility thresholds for the display of layers is recommended when layers have very dense data. A good strategy is to limit the display of these layers to larger scales because the tiles of the smaller scales will not contain the data of these layers, and the time required to produce the tiles will be reduced.
Caching: producing tiles in advance and caching them greatly improves application performance, while reducing JMap Server’s workload. JMap Server can indeed reach its full workload capacity when several users are navigating through large and complex projects in the applications.
JMap server memory: influences the performance of tile production. Increasing the memory allocated to the JMap server can accelerate tile production.
In JMap, forms are used for attribute queries to enter the search parameters, to enter attribute values of editable layers and to manage data stored in databases. This is always done in relation with the elements of a layer.
The JMap administrator designs the forms using the . Afterwards, users can use them in JMap Pro, Web, NG and Survey.
Like data editing forms, attribute query forms are created using the . They allow the users to enter query parameters.
Each form component is therefore associated with a parameter of the query ($param1, $param2, etc.).
Unlike the other types of forms, they cannot be divided into sections. In addition, the Photo components are not available for this type of form.
These forms are created when configuring attribute queries, by clicking on Form layout.
When creating an attribute query form, it is important to consider which parameters are required and which are optional in the query definition. For instance, if Required is not selected for a form component, the query must consider this parameter as optional.
Refer to the section for more information on optional parameters in queries.
There are two aspects to organizing layers in a project:
Order of appearance of the layers on the map. Layers at lower positions are drawn first and layers at higher positions are drawn at the end. Top layers can hide elements of bottom layers.
Logical hierarchy based on the nature of the layers. In other words, groups and subgroups of layers that have a logical relationship. For example, there could be a group of layers related to roads, another to hydrography, and another to census. Organizing them in groups makes it easier for the users to work with layers.
You can set the layer order in the Layers tab and the layer hierarchy in the Layer groups tab of the project configuration interface.
In both tabs you can grant permissions to selected layers. The section provides details about the permissions.
To order layers of a project, open the tab titled List. This section presents the layers in their order of appearance on the map. The lowest position is the first layer to be drawn on the map.
To change the order, you must use the Modify menu located at the top of the column displaying the position of each layer. You can also select one or more layers and move them using the available options (Move up, Move down, Move at…, etc.). The option Reorder layers opens a window displaying all the layers that you can reorder using drag-and-drop actions.
To organize layers in groups, open the tab Layer groups. This section presents the current hierarchy of layers.
By default, all layers of the project are in one unique group called Layers.
To create a new group, press Create group. Fill the layer group parameters as described below:
Once groups have been created, you can move layers towards these groups using the Modify menu located at the top of the column displaying the position of each layer.
You can synchronize the project with JMap Cloud, the cloud based platform developed by K2 Geospatial.
Beforehand, you must connect to JMap Cloud. The section offers details on this subject.
Project properties, layers with their associated spatial data sources, order and hierarchy of layers are reproduced in JMap Cloud.
To synchronize the project with JMap Cloud:
In the project configuration interface, press Sync with JMap Cloud…. A window opens offering you two actions: Copy project: A copy of the project layers (configuration and data) and their spatial data sources is created in JMap Cloud. No JMap Server → JMap Cloud link is created. When a layer is updated on JMap Server, the data is not synchronized with JMap Cloud. Synchronize project: A copy of the project layers (configuration and data) and their spatial data sources is created in JMap Cloud. A JMap Server → JMap Cloud link is created. When a layer is updated on JMap Server, the data is automatically synchronized with JMap Cloud. The window offers two options for the project in JMap Cloud: Create new project: You can specify a new project name that will be used in JMap Cloud. If the project uses multiple languages, the name specified here will replace the default language value. All translations are synchronized. Replace Project: You select the JMap Cloud project that will be overwritten and replaced by the project you are copying or synchronizing.
Select the options that suit you and press OK. If you selected Copy, the Status indicates that the project has been copied to JMap Cloud. This icon allows you to redo the synchronization. If you selected Synchronize, the section displays the following information: Id: Identifier of the project in JMap Cloud. Status: The status of the project creation in JMap Cloud. Last update: Indicates the last time the project was synchronized. Automatic synchronization: Indicates that the synchronization is automatic. Press to remove the JMap Server → JMap Cloud link for the project. The JMap Cloud project is not deleted. Press to start synchronizing the project with JMap Cloud. Once the project is synchronized with JMap Cloud, the icon appears in the list of project layers, in the JMap Cloud column.
Initiates the creation of a new layer. Refer to .
Allows you to duplicate or reference a layer from another project located on the same server or on a different JMap Server. Refer to .
Allows you to import layers one by one from a project exported from another JMap server. Refer to .
Launches the preparation of the vector data cache for the selected layers. Refer to .
Allows you to edit certain layer parameters in batches. The section provides details about this topic.
Check New Value to enable the antialiasing feature. Uncheck New Value to disable the antialiasing feature. The section provides details on this parameter.
The section provides details on this topic.
The section provides details on this topic.
The section provides details on this topic.
Name
Enter a name for the new group. The name must be unique.
Description
Optionally enter a description for the new group. This description will be visible to users.
Visible
Makes the group initially visible when the project is opened. All visible layers inside the group will be displayed.
Always listed
Ensures the group is always listed (displayed in the layer management window ) even if it contains no layer. By default, empty groups are not listed. A group can be empty if it contains no layer, if all the layers it contains are not listed or if the user doesn’t have the permission to see the layers of the group.
Image
This option allows you to select an image (an icon) to display with the group of layers.
Press Choose to open the file browser and select the image file.
The image size should not exceed 100*100 pixels.
This option is only available for JMap NG applications. Other application types do not display the image.
Languages
Available languages
Select the languages that will be available for the project. At least one language must be selected.
Default language
Choose the default language among those that are available. When you enter text in the various configuration sections of the project and layers, you must enter it in the default language.If the user’s language is not supported for the project or if translations are missing, JMap will automatically use the default language.