Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
This JMap extension adds edition tools to a JMap Pro application. These tools allow you to add and modify elements and their attributes on editable layers. They also allow you to perform geometrical operations on the elements of all layers (calculating intersections, unions, buffers, etc.).
Only one layer can be edited at a time.
All edition operations are performed on that layer.
To edit another layer, this layer must be selected beforehand.
Edition tools function differently, depending on the layer's characteristics.
This layer exists in every JMap project. It is the default editable layer. It offers unrestricted edition functionality by allowing you to mix different types and styles of elements. It does not have any attributes (descriptive data), therefore it is impossible to add attribute data to elements that are drawn.
Edition operations performed on this layer are not persistent, meaning they will be lost when the session terminates if they are not exported. To save this data, two options are possible:
Creating a context with an option to save annotations. The edited elements will become available again when the context is opened.
Exporting towards a file (shp, mid/mif, kml or wkt) on the local workstation using the JMap Exportation extension. The data file can be reopened using the JMap Importation extension.
Edition operations on the Annotations layer can be useful to create rough sketches and annotations in a simple and less restrictive way.
Editable layers allow you to edit data, which includes adding, moving, modifying and deleting geometries as well as entering or modifying their attribute values.
The JMap administrator can grant a user the permission to modify the contents of one or more layers within a project.
In addition, a user can create personal layers directly in the Pro application if the JMap administrator grants that user permission to do so, and the administrator can also grant other users permissions to edit those layers. In both cases, editing data is done in a similar way.
Editable layers are more structured than the Annotations layer. Each one has a unique element type and other types of elements cannot be added. They also have a defined set of attributes, which will be present on each element of the layer. Lastly, an editable layer has one or more styles (depending on the scale) that will be applied to all of the layer's elements.
Performing edition operations on an editable layer is subject to the layer's particularities. For instance, any drawing tools for element types that are incompatible with the layer will be deactivated. Interfaces to modify the style of incompatible elements will also be deactivated.
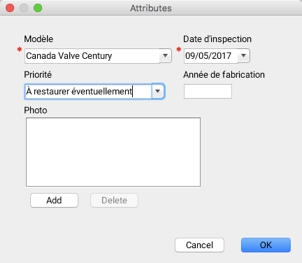
Entering the attributes of new elements is done using a form that displays when each element is added. You can enter attribute values on this form. In editable layers offered by the JMap administrator, some attributes are required and others are optional. The form can only be closed once all required attributes have been populated. In personal layers, all form attributes are optional.
It is also possible to open the attribute entry form by right-clicking on a map element.
For personal layers and editable layers that have a basic form for entering attributes, editing attribute data can also be done using the layer's elements explorer.
This feature is not available for editable layers that have complex forms, with well-defined data formats.
The Edition extension's graphical interface is made up of several parts, including functions that can be accessed through the Tools menu and the context menu, a toolbar offering spatial operations and a dockable window that provides access to the drawing tools.
The JMap Edition extension allows users to add and modify map elements in the JMap Pro application.
It also allows you to perform a number of graphical and geometric operations on map elements.
Combined with JMap's collaboration functions, such as editable layers and map contexts, the Edition extension proves to be a highly useful tool.
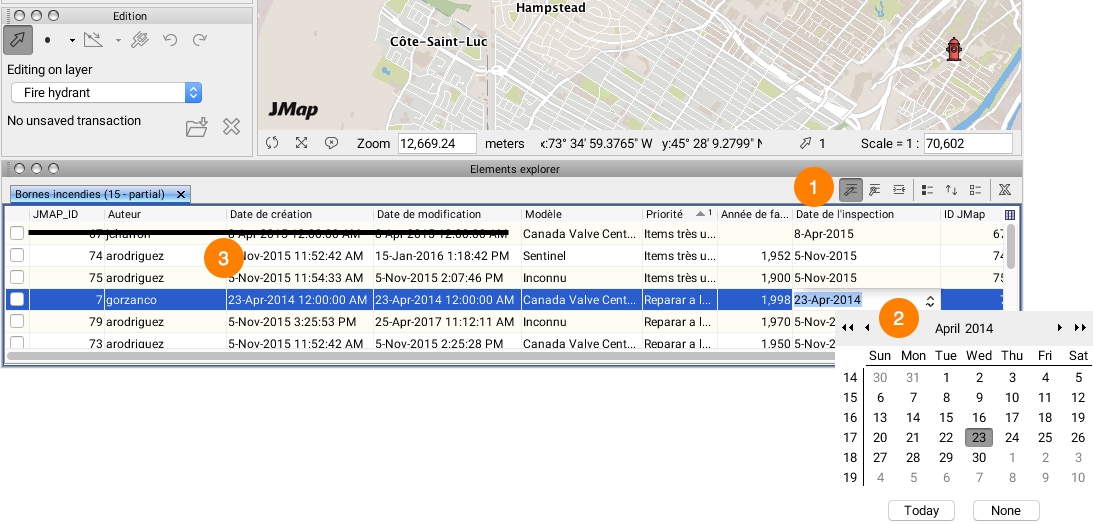
To begin editing attributes, you must first enable attribute data edition in the explorer by clicking on the icon and then clicking in the cell containing the data to modify.
1
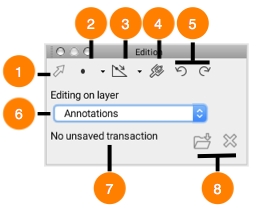
Edition selection tool, used, among other things, to move editable elements.
2
Drop-down menu providing access to various drawing tools.
3
Tools to perform operations on element nodes; used to add, move, and delete nodes.
4
Button allowing you to access the style configuration interfaces of elements.
5
Undo and Redo buttons. Allow you to undo and redo all edition operations one by one.
6
Allows you to choose the layer to edit. Only one layer can be edited at a time. • Annotations layer: This layer is always present and is used by default for the elements that are drawn. All types of elements can be added to this layer and it does not have any attributes. • Editable layers: If the JMap administrator gives you permission to modify the contents of one or more layers of a JMap project OR if you add personal layers to your project, these layers will all be displayed in this list. Edition will be limited according to the properties of the selected layer (element types, element styles, attributes, etc.).
7
Number of unsaved transactions on the server. Only used with editable layers.
8
Allows you to save or discard edition operations. When working on the Annotations layer, discarding changes will delete the layer's entire content. When working on an editable layer, only the changes made since the last save will be discarded.
The Edition extension offers two types of spatial operations: geoprocessing and spatial tools.
Geoprocessing concerns the set or a selection of the elements of the involved layers and their result is a set of new geometries added to the Annotations layer.
The operations performed by the Spatial Tools concern the elements selected beforehand and their result is one or more new geometries that are added to the Annotations layer.
The layers attributes are not retained in the results (the Annotations layer has no attributes).
The elements resulting from the operations can be selected and copied into other layers using the Edition tools and the context menu.
When you perform spatial operations on editable layers, you can hold down the CTRL key to retain only the result of the operation, that is, by automatically deleting the editable elements that were selected.
1
2
Click in an editable cell to enter the new attribute value. Some cells have their own entry interfaces (a calendar for a date attribute, for instance). Validation rules on the type of data entered will be applied after the data is entered.
3
Some system attributes cannot be modified. These attributes are automatically populated by JMap and used for management purposes.
The Edition extension's selection tool is used to select map elements in order to perform edition operations (geometric operations, duplication, etc.) or to move elements.
Although JMap's other selection tools can also be used in most cases, only the Edition selection tool allows you to move editable elements that are selected.
Editable elements that are selected have black grab points on the nodes.
To move an element:
Enable the tool by clicking on .
Select the element.
Drag and drop it to the desired location.
Node operations allow you to add, move, and delete the nodes of editable elements.
Allows you to move one or more nodes of the selected editable elements. Note that this tool also allows you to select elements. To move a node :
Enable the tool by clicking on .
Position the cursor close to the node and it will be highlighted.
Drag and drop the node to the desired position.
To move several nodes simultaneously while maintaining the topology:
Enable the tool by clicking on .
Select the desired element(s).
Press and hold the SHIFT key and select the nodes that must be moved by clicking or drawing a box. The selected nodes will be highlighted.
Drag and drop the selected nodes to the desired position. All selected nodes are moved simultaneously.
Allows you to add a new node to a selected editable element. Note that this tool also allows you to select elements.
Position the mouse pointer on one side of the element and a yellow dot will appear to show the position of the new node.
Click to confirm.
Allows you to delete an existing node from the selected editable object. Note that this tool also allows you to select elements.
Bring the pointer near the node to be deleted and it will be highlighted.
Click to confirm.
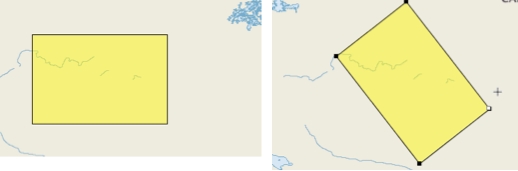
Allows you to rotate polygon and line elements around their center.
Select one of the element's points.
Rotate it.
Release the point when you reach the desired position.
Drawing tools are used to draw map elements on a layer. Only the layer that is selected to be edited can receive the elements that are drawn.
Snap functions are available with edition tools. For more details, refer to the JMap Pro User Guide.
Enabling the icon allows you to modify the cells.
Click on to enable the tool.
Click on to enable the tool.
Click on to enable the tool.
Point Add a new point by clicking on the map.
Point by coordinates Add a point using specific X and Y coordinates.
Freehand Allows you to draw freely on the map, as if using a pencil. 1. Click and hold the left mouse button to draw. 2. Release the button when you are finished.
Line Add a simple line by clicking on the map to define the first point and clicking on it again to define the second point and complete the line.
Multiline Add a new multiline (line with 1 or more segments). 1. Click on the map to define each of the nodes that will form the ends of the segments. 2. Double-click or press the space bar to complete the drawing.
Polygon Add a new polygon on the map. 1. Click on the map to define each of the nodes that will form the ends of the segments. 2. Double-click or press the space bar to complete the drawing.
Box Add a new rectangle on the map. 1. Click to define the first point. 2. Click again on the desired location to define the second point and complete the box.
Ellipse Add a circle on the map. 1. Click to define its central point. 2. Click again to complete a circle of the desired dimension. NOTE: The circle can be changed to an ellipse with radii of various lengths.
Bubble Add a bubble with text on the map. 1. Click to determine the position that will be pointed by the stem of the bubble. A window appears, allowing you to enter the text that will be inserted in the bubble (one or more lines).
Label Add text directly on the map. 1. Click to define the insertion point of the text (upper left corner of the text). A window appears, allowing you to enter text (one or more lines) to be added on the map.
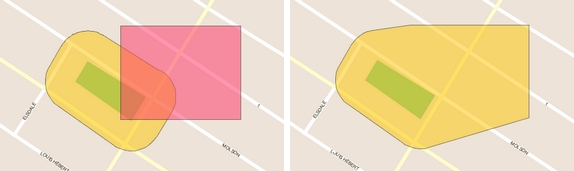
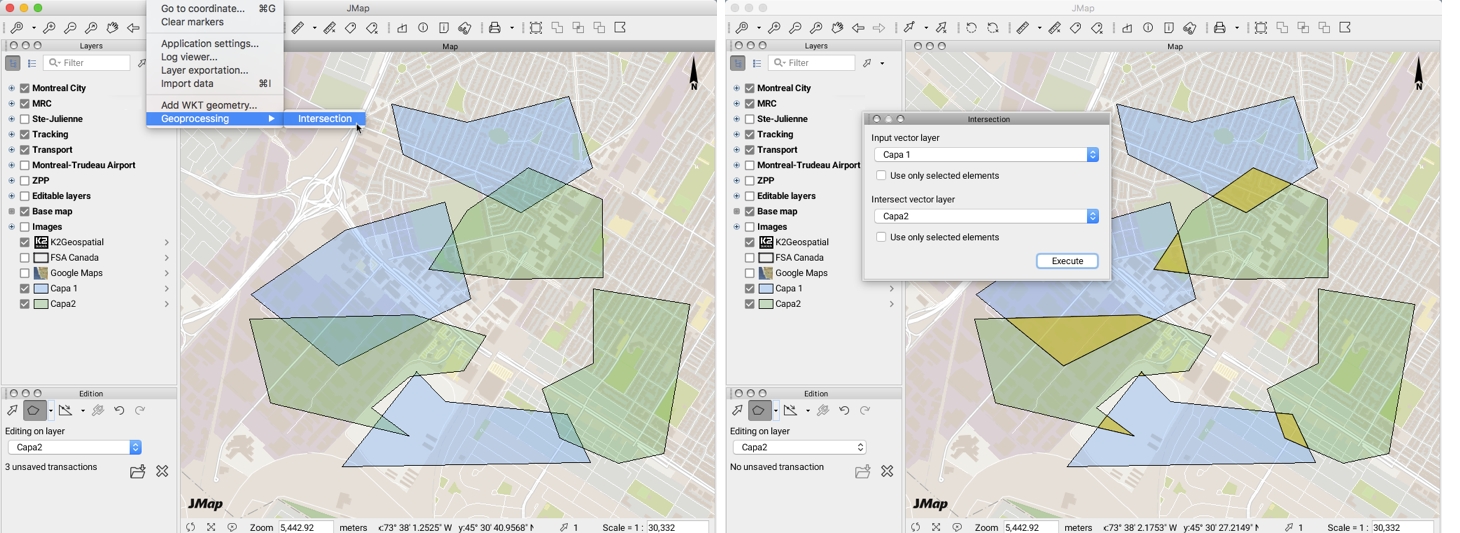
You can intersect the whole or a selection of the elements of two layers:
Select the Intersection function from Tools -> Geoprocessing in the menu bar.
From the drop-down menus, select the layers whose elements will be intersected.
Press Execute. To intersect the selected elements, check the relevant box. The resulting elements of the intersection appear colored and are added to the Annotations layer. These are new geometries resulting from the individual intersection of each of the geometries of the first layer with each of the geometries of the second layer.
You can then copy them to another layer displayed in the application if you have permissions to add elements to it.
Layers geometries can be edited using editing tools and specific functions related to WKT format features. The user must have permissions to edit the layer data.
Editing tools are accessed from the dockable Edition window and include tools for drawing cartographic elements (points, lines, polygons, texts, etc.), a selection tool and tools for adding, moving and erasing nodes.
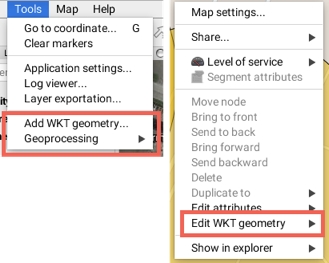
WKT functions are accessed from both the Tools menu and the context menu.
The map's pop-up menu offers options that are specific to the Edition extension when it is included in the application. Right-clicking opens this context menu.
The vertical position of the elements on the Annotations layer can be modified. This allows you to control which element must be displayed above the others, for instance. Elements can be moved one position at a time or can all be sent to the front or back. Elements must first be selected.
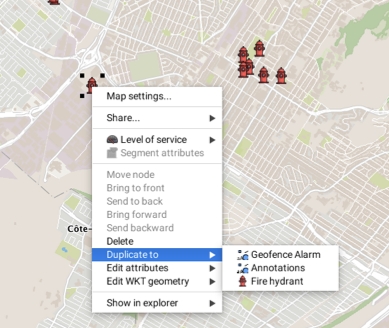
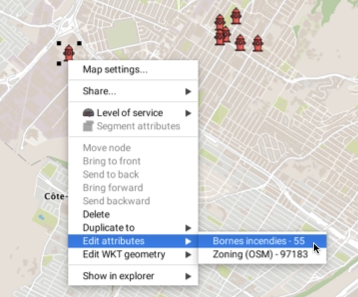
Elements found on a given layer can be duplicated towards another layer. The menu displays a list of available destination layers. You must select the destination layer of your choice. When elements are copied from one layer to another, the style of the destination layer is applied to these elements. If the attributes are the same for both layers, the attribute values will be copied with the element.
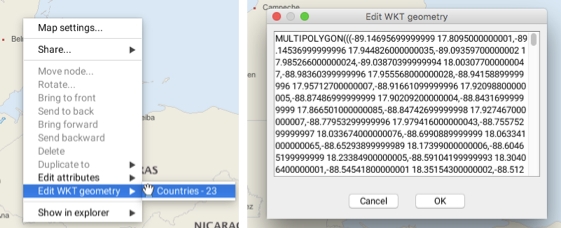
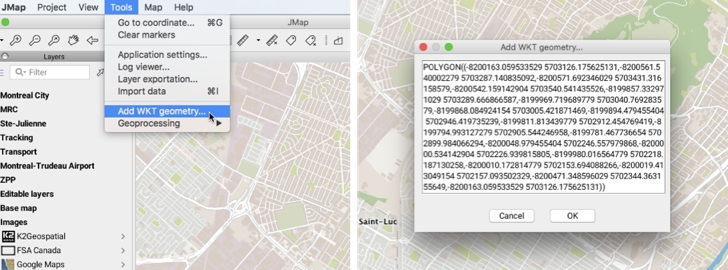
The JMap Pro user can add and edit WKT geometries.
The Well-known text is a format defined by OGC to represent geometric features such as points, lines, polygons, TINs, and polyhedra using two- or three-dimensional coordinates. The format is also used to represent information about features such as the coordinate system (fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Well-known_text, www.opengeospatial.org/standards/sfa).
The function is available through Tools -> Add WKT Geometry in the menu bar. A window deploys and allows to write the coordinates of the elements to be added.
Elements are added to the Annotations layer. They can be saved in a context or they can be selected and duplicated in other editable layers, using the context menu. This menu also allows you to delete elements or change their vertical position.
The context menu also offers the possibility of editing WKT elements. The Edit WKT geometry function displays the elements of the layers found at the map point where the context menu is open. Select one of the elements to open the window containing the element's coordinates and data. If you have the appropriate permissions, you can edit this data.


Spatial operations are performed on one or more selected elements.
A spatial operation results in a new geometry added to the Annotations layer.
When you perform spatial operations on editable elements, you can press and hold down the CTRL key to keep only the results of the operation, i.e. automatically deleting the editable elements that were selected.
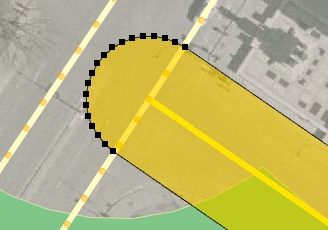
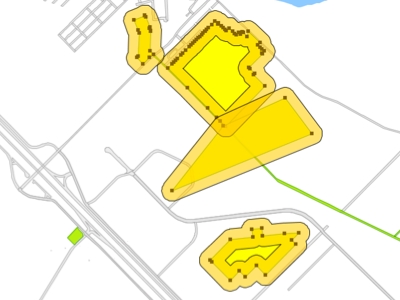
Creates a buffer zone around the selected map elements.
You can create the buffer zone for each element individually or a buffer zone for all elements.
Select the desired elements and press.
You must then specify the size of the buffer, i.e. the maximum distance between any point of the buffer and the selected elements. The size can be negative, in which case the buffer can be smaller than the selected elements. The size of the buffer is indicated in the map's unit of distance.
Keep Generate a buffer for each selected element checked if you want this type of buffer.
Specify the precision of the buffer arcs, in degrees.
Press OK. The example shows a 100 m buffer around each park in a city.
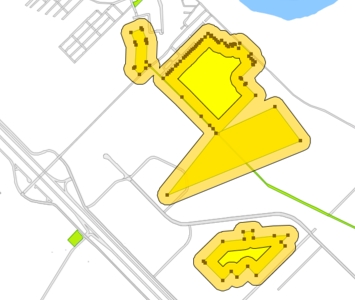
Uncheck Generate a buffer for each selected element if you wish a single buffer to be generated for the set of selected elements.
Specify the precision of the buffer arcs, in degrees.
Press OK. The example shows a 100 m buffer around parks in a city.
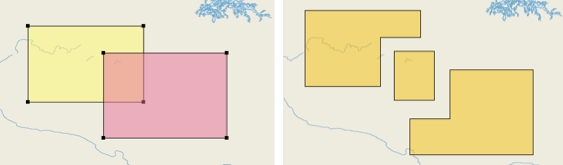
Creates a new element by uniting the selected elements.
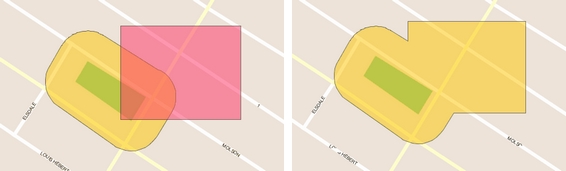
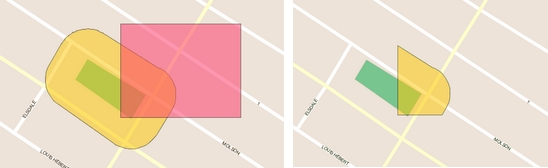
Creates a new element that is the intersection of the selected elements.
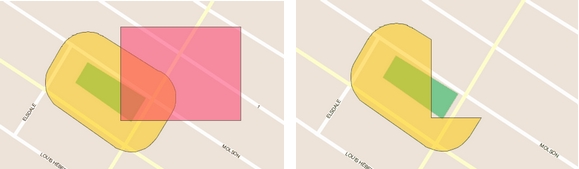
Creates a new map element that is the difference between the first selected element and the others. In other words, all elements are subtracted from the element that was selected first.
Creates new elements resulting from the intersection of two polygons.
Creates new elements resulting from the splitting of a polygon using a line.
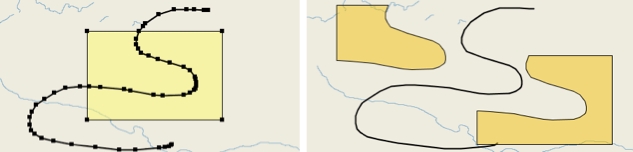
Creates a new element that is the smallest convex polygon that entirely covers the selected elements.
Select at least 2 elements and press .
Select at least 2 elements and press .
Select at least 2 elements and press .
Select the two polygons and press .
Select a polygon and a line that come from two different layers and press .
Select the elements and press .