Style
The style of a layer determines the graphical representation of its spatial elements on the map. For example, the style of a line is determined by its thickness, color, dash pattern, etc. In JMap, each layer can have multiple styles. The style used depends on several factors.
Different styles can be configured for different scales. For example, a layer can have a single style for all scales while another layer can have one style for scales greater than 1:20000 and another style for scales smaller than or equal to 1:20000.
Layers also have selection styles. These styles are used to display selected elements at different scales. The selection styles are generated automatically from the layer styles but they can be customized for each layer.
The presence of thematics on a layer will override the layer styles.
When a thematic is active on a layer, the style of each element is determined by the value of its attributes and the thematic's parameters. See Thematics for more information.
As of JMap Server Jakarta, polygon layers with three-dimensional representation are supported in JMap NG applications. This representation of a third dimension is called an extrusion, and it can be configured when defining the style of the layer. The Extrusion section explains the details of this configuration.
Managing layer styles
You can define one or more styles for a layer.
If there are many styles, each one will be used within a certain range of scales.
By default, one style exists for each layer and it covers the full possible scale range.
The Style tab in the layer configuration interface allows you to manage the layer's styles.
To add a new style, press Add. In the style configuration interface, you must define the maximum scale from which the new style will be used. Its minimum scale will automatically be set to infinity or to the maximum scale of the next style.
To remove a style, select it from the list and press Delete.
The greater scale style cannot be deleted.
When deleting styles, the remaining styles will be adjusted to cover the full possible scale range.
Once you have configured one or more styles, you can click on Create template (located to the right of each style) to create a new style template from one of the layer's styles. The style template will automatically be linked to the layer. See Style Templates for more information.
JMap Pro users can change the style of layers and save their changes by creating cartographic contexts. These contexts can be shared with other users and made public to all users who access the application.
JMap Web and JMap NG users can save a map by creating a customized map.
When the JMap administrator modifies the style of a layer, the JMap Pro, JMap Web and JMap NG users working with contexts may not be able to view the style changes made by the JMap administrator. To force the update of the layer style in the contexts, click on Force update... (located to the right of each style). By doing so, the style changes will be reflected in all the contexts of JMap Pro applications and in all the customized JMap Web and JMap NG maps that contain the layer.
Creating or Modifying a style
You have the option to use an existing style template or to configure your own style. If you want to use a style template, click on Use a style template. You will then choose to refer to it or to copy it.
If no style template is used, you need to configure the parameters that will define the style. Start selecting Default style.
Style configuration interfaces are different depending on the type of element (points, lines, polygons, text, etc.). Some style parameters are common to many element types but others are specific to certain types.
Antialiasing is a method of representing perfect, continuous vectors on imperfect, discontinuous display devices so that they look as perfect as possible. In every style configuration section in JMap Admin, antialiasing is enabled by default, which improves the appearance of your maps. However, display performances are reduced when antialiasing is enabled, so use it judiciously.
The following figure shows an example of a polygon border with antialiasing (left) and without antialiasing (right).
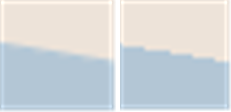
Partial object transparency can be used for every type of map element. A map element with a transparency value of 0% will be completely opaque while one with a 100% value will be invisible.
The following figure shows an example of a polygon with a transparency value of 50% (left) and one with a transparency value of 10% (right).
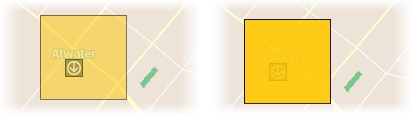
Styles for points
Symbol
Select the symbol that will be used to represent the elements. The symbol can be a vector symbol or an image.
Vector symbols are provided with JMap and offer special features. They can be resized without distortion and their border and fill color can be modified. However, they cannot be customized easily.
JMap offers image libraries, which include SVG images. These image libraries are accessed under the Images tab. You can also provide your own image libraries. Their quality will be decreased if they are resized, unless you use SVG images.
To provide your own images, place them in the following directory:
JMAP_HOME/JMapAdmin/icons
Supported image formats are svg, gif, png and jpeg. If subdirectories are created, they will be seen when browsing the image directory. This allows you to organize your image library.
You can also upload new images by clicking on ![]() in the symbol selection window. The maximum image size is 100 Mb.
in the symbol selection window. The maximum image size is 100 Mb.
Size
Specify the size of the symbol. A value of 1 corresponds to the original size of the symbol or image.
Proportional size
Select this option if you want the size of the displayed symbols to vary in proportion with the map scale. You must enter the reference scale that will display the normal size of the symbols.
Use antialiasing
Select this option to activate antialiasing.
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the symbol.
Offset (x,y)
Adjust the original point of the symbol by offsetting the symbol by X and Y according to the specified values. The original point corresponds to the exact coordinates of the point element.
Rotate symbol with the map
Select this option to have the symbol rotated when the map is rotated. If this option is not selected, the symbol will always have its default angle, regardless of the map rotation.
Rotation
Specify the rotation to apply to the symbol.
Border thickness
(For vector symbols only) Specify the border thickness of the vector symbol.
Border color
(For vector symbols only) Specify the color of the lines of the vector symbol.
Transparent fill
(For vector symbols only) Select this option to have the inside of the vector symbol completely transparent.
Fill color
(For vector symbols only) Specify the color of the interior of the vector symbol.
Styles for lines
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the line.
Arrow type
Specify the arrow option to use: None: No arrow. Forward: Place an arrow on the line pointing toward the last point of the line. Backward: Place an arrow on the line pointing toward the first point of the line.
Arrow position
If an arrow is used, determines the relative position of the arrow. A value of 50% places the arrow in the center of the line.
Line thickness
Specify the thickness of the line, in pixels.
Line color
Specify the color of the line.
Stroke style
Specify the stroke style (dashed, solid, with border, etc.) to use to draw the line. JMap provides many stroke styles.
Border thickness
If the line has a border, specify its thickness.
Border color
If a line stroke with a border is used, specify the color of the border.
Styles for polygons
Use antialiasing
Select this option to enable antialiasing.
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the polygon.
Transparent fill
Select this option to have the inside of the polygon completely transparent.
Fill color
Specify the color of the interior of the polygon.
Stroke style
Specify the stroke style (dashed, solid, with border, etc.) to use to draw the border of the polygon. JMap provides many stroke styles.
Border thickness
Specify the thickness of the borders of the polygon.
Border color
Specify the color of the border of the polygon.
Pattern
Specify the fill pattern to use. JMap provides many patterns.
Pattern color
If a pattern is used, specify the color of the pattern.
Transparent pattern fill
If a fill pattern is used, select this option to make the pattern background completely transparent.
Styles for annotations
Use antialiasing
Select this option to enable antialiasing.
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the text.
Font
Specify the font used to display the annotation text.
Bold
Select this option to use bold text.
Italic
Select this option to use italic text.
Underlined
Select this option to use underlined text.
Striked through
Select this option to use strikethrough text.
Outlined
Select this option to use outlined text. Outlined text has an outline that may be of a different color. This helps make the text on the map more readable.
Outline color
If outlined text is used, specify the color of the outline.
Text color
Specify the color of the text.
Styles for images
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the image.
Selection style
There is a selection style for each style of the layer. The selection styles are used to represent the elements when they are selected on the map. By default, the selection styles are generated automatically using the layer's basic styles and the project's default selection color.
To modify the selection style, unselect the Generate from default style option and adjust the style parameters as needed.
Extrusion
The style of polygonal layers allows you to configure a three-dimensional representation of the polygons.
In the configuration interface for the layer's style parameters, under the Extrusion section, check Enabled to enable extrusion in JMap NG applications. This function is disabled by default.
Click on Configure to open the extrusion configuration window.
Base
Select the numeric attribute that indicates the height of the terrain on which the polygon is found.
Height
Select the numeric attribute that indicates the height of the polygon.
Transparency
Specify the partial transparency of the extruded polygons.
Click on Delete to delete the extrusion configuration.
Analysis
In addition to configuring the style of a layer, you can also create graphical representations to analyze the distribution of point data.
Clustering
Clustering, as its name implies, creates clusters of points on the screen. Special symbols are used to graphically represent these clusters on the map and display the number of elements they contain.
Distance
Minimum distance (in pixels) between 2 points in order for them to form a cluster.
Minimum elements
The minimum number of elements required to create a cluster.
Symbol
Symbol used to represent a cluster on the map.
Label
The settings of the label (font, color, etc.) that will display the number of elements in a cluster.
Heat maps
Heat maps are used to graphically represent the concentration distributions of a type of object or event on the territory. The more the color of a zone is intense, the more the concentration is high.
Radius
The radius used to display the density map around each point.
Weight
Numeric attribute that determines the weight of each point to display the density map. The more the weight is high, the more the color is intense. This parameter is optional.
Opacity
Determines the degree of opacity for the display of the density map.
Intensity
Defines the intensity of the colors based on the concentration of points. If the intensity is lower, more points will be needed to produce intense colors.
Display points
Allows you to display the points of the layer under the density map. The points will be hidden by the density map if the opacity is very high.
Mis à jour